Removable Insulation Covers for Industrial Valves – What to Look For
Comments Off on Removable Insulation Covers for Industrial Valves – What to Look For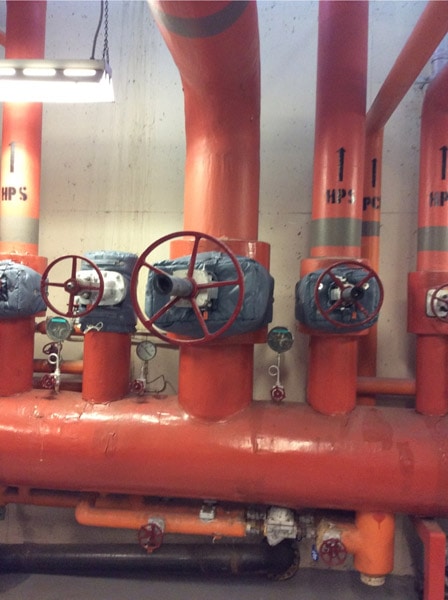
Valves are one of the most common parts to cover in the petrochemical, chemical, and oil and gas industries. Like process line piping, valves often need to be insulated to minimize heat loss for energy efficiency or to keep the contents of the materials flowing through the valve at a desired temperature. In addition, insulation blankets keep the valve parts from freezing up in cold temperature operations. However, unlike process line piping, which is often insulated with permanent insulation or cladding, valves generally must be kept accessible to maintenance personnel in case they need servicing or are required during an emergency situation. This makes valves ideal candidates for removable / reusable insulation covers.
Removable Valve Covers – What to Look For?
When dealing with removable insulation covers, one size does not fill all. Here are some variables that Firwin’s design team considers when designing removable insulation covers:
Proper fit: Valves can come in a variety of configurations—gate valves, flow valves, butterfly valves, etc.—with a large variety of makes, models, and sizes within each category. Each of these has their own unique geometry, and a custom designed insulation cover should precisely match the part for which it is intended. Valve orientation or presence of adjacent valves or piping can also affect the final blanket design. In cold weather climates, valves are also subject to glycol, water, steam, or electric heat tracing. Properly positioned cut-outs are essential for an insulation cover to fit properly and function as intended.

Insulation thickness: While removable insulation covers typically contain a 1” thick insulation material, this thickness can vary depending on the needs of the particular application. For very small valves or where clearances are an issue, a thinner 1/2” thick insulation is often called for. On the other hand, there are instances where a thicker insulation is needed due to high heat or for sound attenuation. In addition to requiring a thicker insulation, sound attenuation needs a multi‐layered construction, with an additional layer of sound dampening material. These multi‐layered covers can get as thick as 4”.
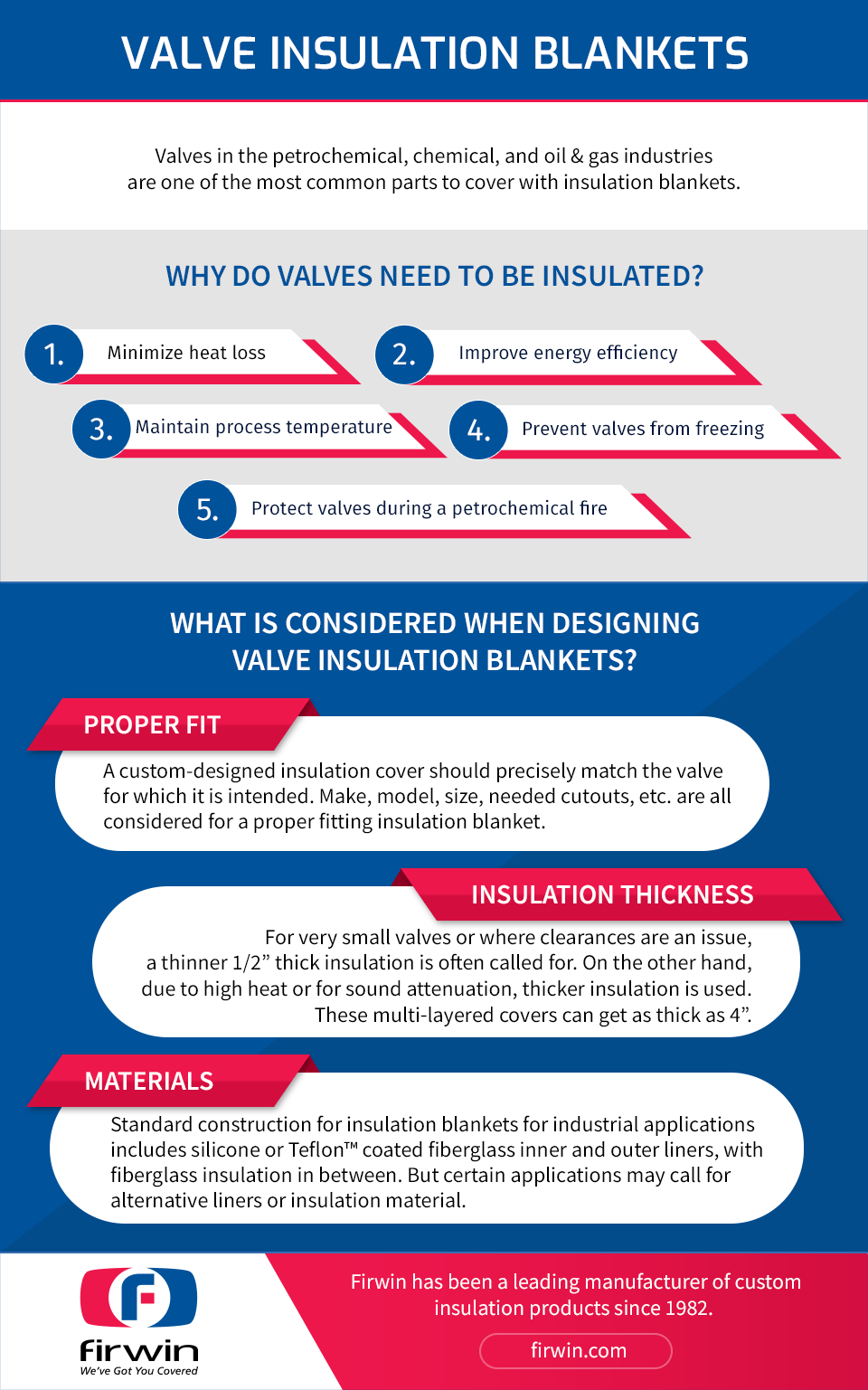
Materials: Standard construction for removable insulation covers for industrial applications include silicone or Teflon™ coated fiberglass inner and outer liners, with a fiberglass insulation in between. But certain applications may call for alternative liners or insulation material. For instance, where temperatures higher than 500°F are present, silicone/Teflon inner liners will not suffice, and a higher temperature alternative, such as Firwin HT, is necessary.
Removable Insulation Covers From Firwin
Since 1982, Firwin has been a leading manufacturer of custom insulation products for piping, valves, engines, and an expansive range of other industrial purposes. Our main product lines include permanent Hard Coat™ composite insulation and removable insulation blankets. Since our inception, we have been offering safe and effective insulation solutions for a variety of industries.
Along with offering top quality insulation products, we are also committed to providing exceptional customer service through sales, installation, and product selection. To learn more about Firwin’s products or to get started on a project with our team, contact us today.
Sound Attenuation Solutions
Comments Off on Sound Attenuation SolutionsDiesel-powered equipment offers some tremendous advantages, but it does come with one consistently difficult challenge: Noise. The ambient noise levels caused by diesel equipment can be deafening, which can pose a substantial safety risk to operators and personnel. Decreasing this risk requires a careful sound attenuation strategy.
While insulation blankets may help to dampen sound, they are often far more effective when combined with specialized sound attenuation material like barriers, panels, or curtains. Firwin’s experts draw on decades of experience in sound management to engineer a solution customized to meet the needs of your facility.
Background: What is Sound?
Understanding sound attenuation technologies requires a bit of background on what sound actually is. At its simplest, sound is a vibration that the ear can interpret based on changes in atmospheric pressure. The level of perceived sound pressure depends not only on what causes this initial vibration but also on the acoustic traits of the surroundings. Some rooms will naturally amplify sound waves while others are specifically designed to absorb and minimize the disturbance before it reaches the ear.
Sound can be quantified in Decibels (dBs), which is especially useful when discussing personnel safety. The human ear can only tolerate certain noise levels without sustaining damage, up to and including permanent hearing loss. OSHA standard 29 CFR 1910.95 dictates the upper limit of tolerable noise as being 85 dBs.
Sound can also be classified by frequency levels, which are interpreted to the ear as different pitches. These vibration frequencies are measured in Hertz (Hz). Isolating and addressing a noise problem requires careful attention to both frequency and volume.
To do this, analysts will break down all present frequencies into eight or nine octave bands. They will then analyze the resulting octave band frequency report in combination with a report of dB ratings in the same room. This provides a full picture of the acoustic situation in the room, allowing an engineer to develop a solution that addresses the specific problem in context of any physical constraints.
Sound Attenuation Materials
Insulation solutions typically combine several materials, each intended to either absorb or block sound. Providing physical barriers in this way can prevent sound leakage and decrease the overall level of sound in a room.
Different materials are better suited to noises of different frequencies. For instance, fiberglass and mineral wool are known to be very effective against high-frequency sounds. Lower frequency sounds are more complicated because they consist of longer wavelengths that are harder to absorb. In these cases, thicker materials and barriers must be used to absorb as much of the wavelength as possible.
Safety is another key consideration for material selection. Sound attenuation is typically necessary in hazardous industrial environments, meaning that any solution must be able to withstand intense heat and other harsh environmental factors. At Firwin, we construct our blankets using only non-combustible materials that conform to MIL and UL fire standards, ensuring that all our products can hold up to extreme temperatures.
Firwin Solutions
Firwin takes pride in offering custom solutions for every client we work with, selecting the most appropriate materials and structures to match the layout and operating conditions of every facility.
 For engine rooms, we typically choose to insulate the walls with tightly packed fibrous glass, mineral wool, or open-cell foam panels, providing effective absorption of high-frequency noise. In other situations, we might opt for a composite such as Firwin BTMM14C. Composites are advantageous when there is a fuller octave spectrum of noise pollution present.
For engine rooms, we typically choose to insulate the walls with tightly packed fibrous glass, mineral wool, or open-cell foam panels, providing effective absorption of high-frequency noise. In other situations, we might opt for a composite such as Firwin BTMM14C. Composites are advantageous when there is a fuller octave spectrum of noise pollution present.
We’ll also consider whether your equipment requires regular maintenance or inspection. If so, we might include removable sound blankets as a part of your solution, making it easy to remove and replace as needed.
We understand that sound attenuation can be complicated, so we’ve created a whitepaper that simplifies material selection for facilities working with diesel equipment. This resource breaks down the most common absorption materials, including comparison charts and tables. It also presents transmission loss and STC information for our composite absorber/barriers used in engine rooms and containers.
To learn more about Firwin’s sound attenuation solutions, download our whitepaper, “Sound Attenuation – Diesel Powered Equipment.” Feel free to contact us with any specific questions.

